

2020-06-18
Laser welding process monitoring can be divided into paraxial type and coaxial type according to the acquisition angle of imaging optical signal. The paraxial type is to form a certain angle with the laser beam, and the signal reflecting the welding process is extracted from the oblique above or one side of the welding pool; the coaxial type is from the welding pool and the hole directly above, coaxial with the laser beam The imaging signal is extracted in the direction of . According to whether there is an illumination source? The visual sensing of the laser welding process can be divided into active and passive. The active type uses the auxiliary illumination light source to perform paraxial or coaxial illumination on the molten pool and the small hole? The passive type uses the radiation light of the plasma as the illumination light or the radiation light of the liquid metal in the molten pool as the imaging light signal.
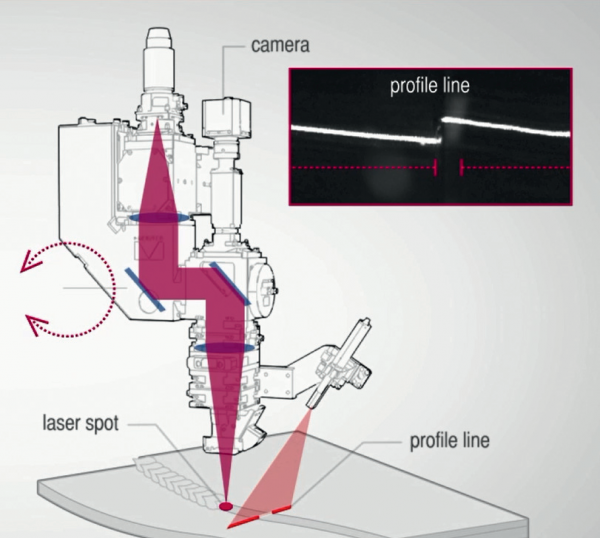

The positioning and installation of the sensor in the rangefinder vision sensing process is relatively convenient and simple. Its image acquisition optical path is also very simple; conventional paraxial illumination is also relatively simple? But the inability to see the plane shape of the small hole is its biggest defect. In addition, the installation and positioning of the rangefinder vision sensor requires a relatively large space.
The coaxial vision sensor in the laser welding process can observe the small hole directly above the small hole and monitor and judge the state of the welding process by processing the collected coaxial visual images of the molten pool and the small hole. Compared with paraxial vision sensor, it has many advantages, such as compact structure, can be integrated with laser output lens, and occupies less space.
The current advanced optical device fabrication technology can effectively solve this problem. For solid-state lasers with short wavelengths such as Nd:YAG, a beam splitter is generally placed in the laser optical path to make the optical signal or laser beam from the molten pool be reflected and deviate to achieve the separation of the coaxial imaging signal and the laser beam optical path; The CO2 laser is generally extracted by passing the imaging light signal from the molten pool through the micro-hole on the focusing mirror, and characterizing the change of the depth of the small hole. This treatment method has great limitations and the treatment results are greatly affected by welding conditions and plasma.
The laser welding quality can be indirectly predicted by studying the penetration of the workpiece, the change of the small hole with the welding speed, and the corresponding relationship between the penetration depth and the width of the small hole and the molten pool through visual sensing. For example, when the penetration state of the weld seam is changed from “not penetrated” or “only molten pool penetration” to “moderate penetration (small hole penetration)” during the welding process, it can be seen that the penetration depth of the laser welding process is Closed-loop control provides a theoretical basis.